what is ketoacidosis Ketoacidosis diabetic dka cetoacidosis deadly invokana coma
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious medical condition that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body is not able to produce enough insulin, resulting in high levels of ketones in the blood. This can lead to an acid buildup in the body and cause a range of symptoms, including vomiting, frequent urination, and confusion. If you or someone you know has diabetes, it’s important to understand the signs of DKA and how to prevent it. Here are a few key things to keep in mind: 1. Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly: If you have diabetes, it’s crucial to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to make sure they are within a healthy range. High levels of glucose can lead to DKA, so it’s important to take insulin or other medications as prescribed to keep your levels in check. 2. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for preventing DKA. When your body doesn’t have enough fluids, it can lead to an imbalance of electrolytes, which can result in DKA. 3. Recognize the symptoms: DKA can cause a range of symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, confusion, and abdominal pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. If you are diagnosed with DKA, your doctor may recommend hospitalization to help manage your symptoms. Treatment typically includes fluids, electrolytes, and insulin therapy to help stabilize your blood sugar levels. In addition to following your doctor’s treatment plan, there are a few things you can do at home to help manage DKA. These include: - Testing your blood sugar levels regularly - Drinking plenty of fluids to stay hydrated - Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains - Avoiding sugary foods and drinks By taking these steps and staying on top of your diabetes management, you can help prevent DKA and maintain your overall health and wellbeing. Remember to always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about your diabetes management. We hope this information has been helpful in understanding more about diabetic ketoacidosis and how to prevent it. Be sure to share this information with friends and family members who may be at risk for this condition. Together, we can all work towards better diabetes management and a healthier future.
If you are looking for What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition like Ketoacidosis, What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition and also Absorb Medicine: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA). Read more:
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - 4 Definition
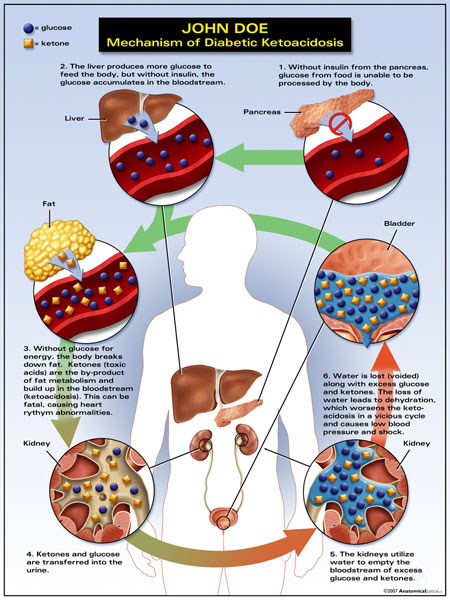 www.allinallnews.comketoacidosis diabetic dka definition diabetes ketosis acidosis sugar dku graphic sepsis insulin
www.allinallnews.comketoacidosis diabetic dka definition diabetes ketosis acidosis sugar dku graphic sepsis insulin
Absorb Medicine: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
 absorbmedicine.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka acidosis diabetes type nursing keto insulin ketosis diabete medicine dm
absorbmedicine.blogspot.comketoacidosis diabetic dka acidosis diabetes type nursing keto insulin ketosis diabete medicine dm
What Is Ketosis? - Perfect Keto Exogenous Ketones
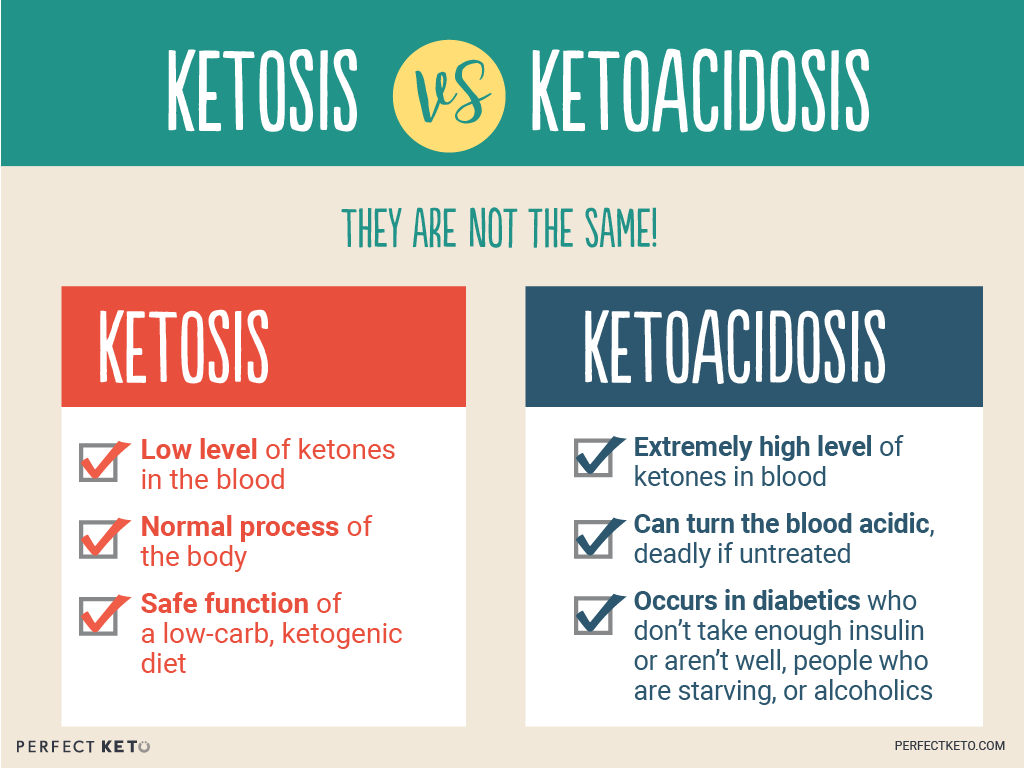 www.perfectketo.comketosis ketoacidosis keto diet vs fasting ketones intermittent ketone ketogenic between symptoms levels dka benefits level fat high long healthy
www.perfectketo.comketosis ketoacidosis keto diet vs fasting ketones intermittent ketone ketogenic between symptoms levels dka benefits level fat high long healthy
Ketoacidosis
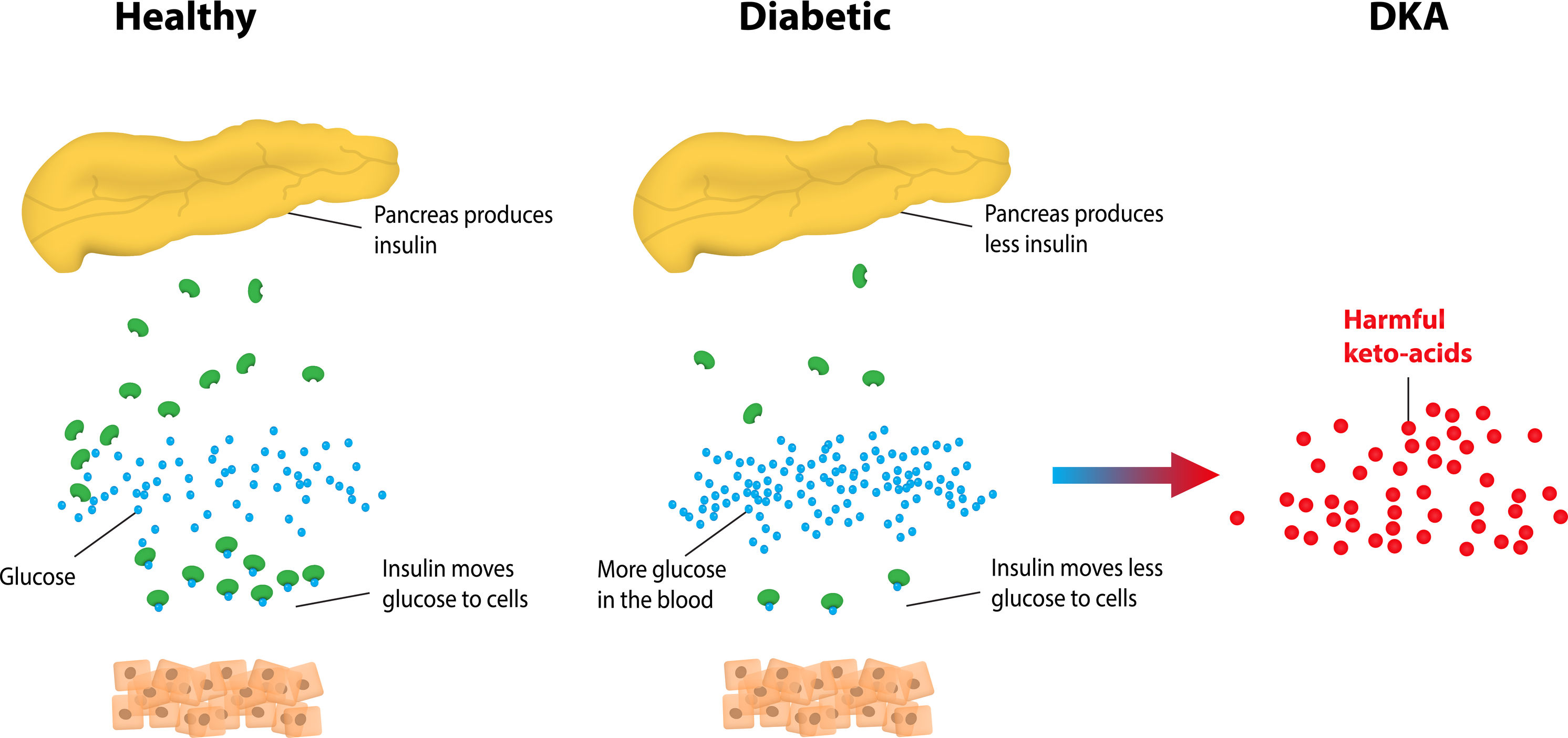 diseasesandconditions.netketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications keytones live risks sugar everyone should
diseasesandconditions.netketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications keytones live risks sugar everyone should
Learning About Ketoacidosis | Wellness Works NW
 www.wellnessworksnw.comketoacidosis diabetic dka cetoacidosis deadly invokana coma
www.wellnessworksnw.comketoacidosis diabetic dka cetoacidosis deadly invokana coma
Ketoacidosis diabetic dka cetoacidosis deadly invokana coma. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka acidosis diabetes type nursing keto insulin ketosis diabete medicine dm. Ketoacidosis diabetes dka diabetic type ketones understanding blood definition symptoms pathophysiology ketogenic diet complications keytones live risks sugar everyone should